使用的configurationProperties含义
在SpringBoot中,当需要获取到配置文件数据时,除了可以用Spring自带的@Value注解外,SpringBoot提供了一种更加方便的方式:@ConfigurationProperties。只要在bean上添加上这个注解,指定好配置文件的前缀,那么对应的配置文件数据就会自动填充到bean中。
application.yml 和 application.properties等方便了我们进行配置的管理和统一,但是在使用的是时候,我们还是通过@Value("${xxxx}")的形式去使用,例如
@Value("${test.name}")
private String name;
@Value("${test.age}")
private int age;
@Value("${test.address}")
private String address;但是使用了@ConfigurationProperties配置之后,可以进一步简化@Value()的使用,最后的结果会变的简单
@Data
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "test")
public class TestConfigurationPropertyBean {
// @Value("${test.name}")
private String name;
// @Value("${test.age}")
private int age;
// @Value("${test.address}")
private String address;
}引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>开始使用
1.在yml文件中写好配置参数
test:
name: lirihong
addres: nanshan
age: 182.声明一个对象
@Data
@Component
//@EnableConfigurationProperties(TestConfigurationPropertyBean.class)
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "test")
public class TestConfigurationPropertyBean {
// @Value("${test.name}")
private String name;
// @Value("${test.age}")
private int age;
// @Value("${test.address}")
private String address;
}添加@ConfigurationProperties注解在类的头部,并加上prefix的前缀,指定查找对应前缀test的配置
bean对象要有get 和set 的方法,所以使用了@Data注解
最后使用@Component 将对象都暴露成一个组件,交给spring去管理,方便其他方法的使用,不推荐使用@EnableConfigurationProperties(TestConfigurationPropertyBean.class)注解
3.编写测试类来进行测试
@SpringBootTest
class StudyApplicationTests {
@Test
void contextLoads() {
}
@Autowired
TestConfigurationPropertyBean testConfigurationPropertyBean;
@Test
public void testConfigurationProperties() {
System.out.println(testConfigurationPropertyBean.getAddress());
System.out.println(testConfigurationPropertyBean.getAge());
System.out.println(testConfigurationPropertyBean.getName());
//System.out.println(testConfigurationPropertyBean.getChinese());
//System.out.println(testConfigurationPropertyBean.getMath());
//System.out.println(testConfigurationPropertyBean.getEnglish());
}
}4、输出结果

5.进阶
有时候如果一个bean对象能尽量的内聚成只有和自己相关的参数属性,那是最好的,这样只需要使用一个@ConfigurationProperties就可以完成配置,但是总有一些情况,比如如果是对象是Controller,牵涉的和对象比较多,这个时候如果使用一个@ConfigurationProperties可能无法完成所有的配置注入,这个时候,还是可以使用原有的@Value配置进行注入值,从而达到效果
application.yml
test:
name: lirihong
address: nanshan
age: 18
score:
Chinese: 98
math: 100
English: 99bean
@Data
@Component
//@EnableConfigurationProperties(TestConfigurationPropertyBean.class)
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "test")
//@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "score")
public class TestConfigurationPropertyBean {
// @Value("${test.name}")
private String name;
// @Value("${test.age}")
private int age;
// @Value("${test.address}")
private String address;
@Value("${score.Chinese}")
private int Chinese;
@Value("${score.math}")
private int math;
@Value("${score.English}")
private int English;
}输出结果
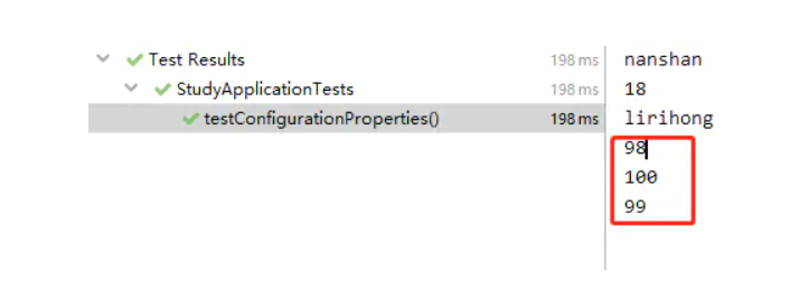
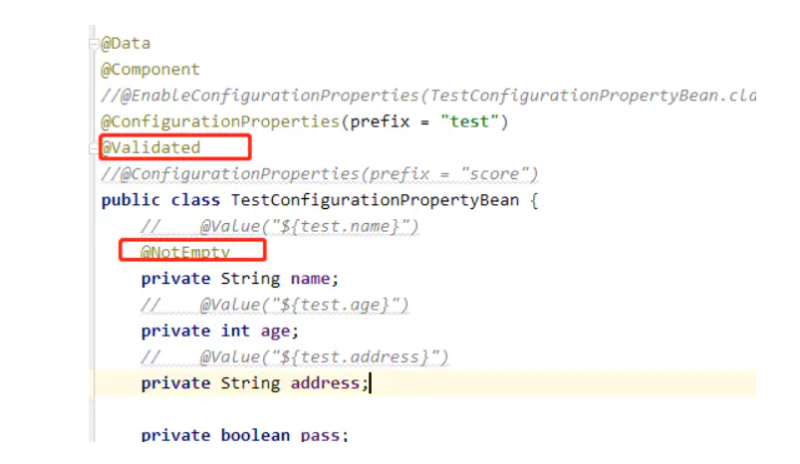
2.加上参数校验@Validated
在类的头部加上@Validated 注解,在字段上加上@NotEmpty等注解,在注入值的时候会自动校验值的参数,不符合则报错
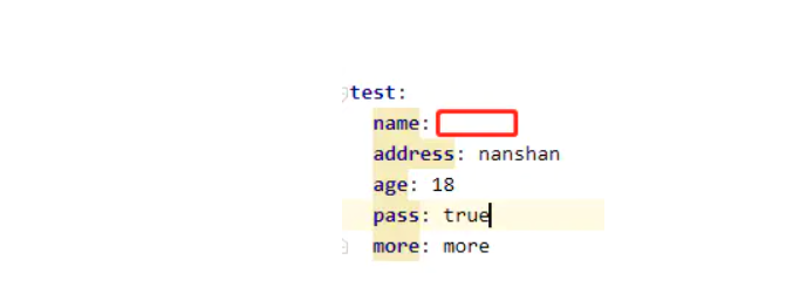
例如 application.yml
bean
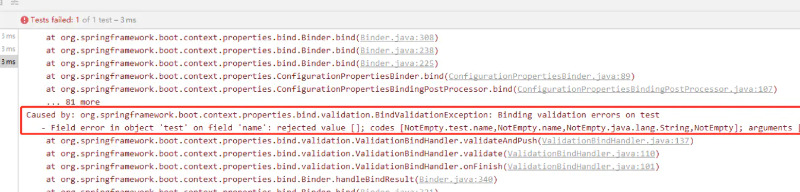
启动服务 就会报错,错误信息中会提示我们是name 属性注入了空值,但是他是不允许为空的
使用该注解可以尽量的查找出在yml中声明了,但是没有用的注解,这样可以简化和删除一些当初设定了但是后面没有用到的注解。默认ignoreUnknownFields = true,即使有多余的配置,也会忽略不管,但是将参数设置为false之后ignoreUnknownFields = false,服务启动的时候就会全部查找所有的yml 或者properties配置进行匹配,发现存在没有匹配的,都会报错
yml文件
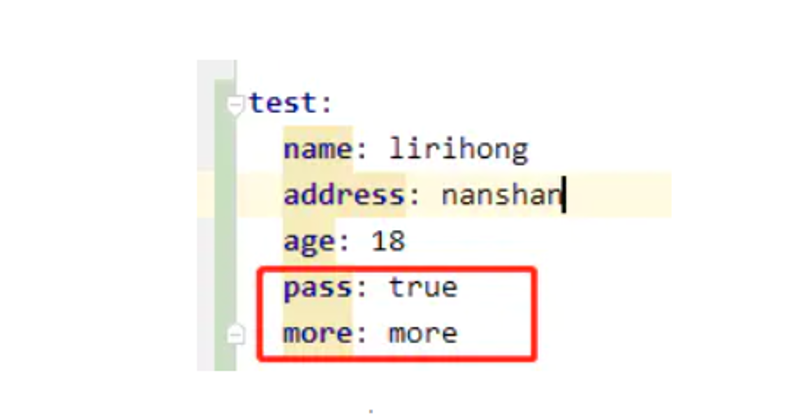
bean
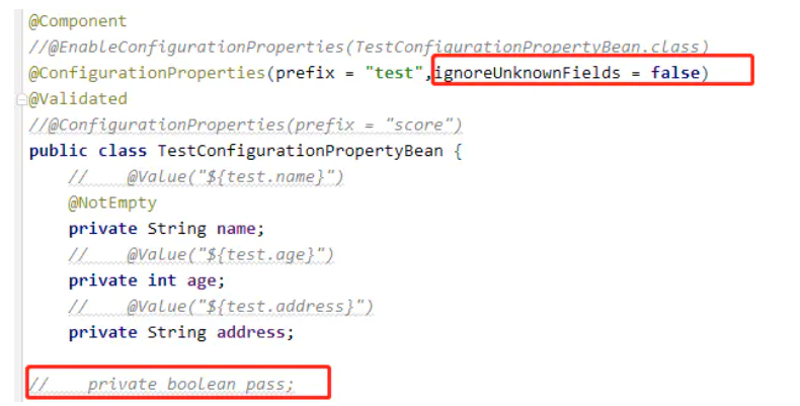
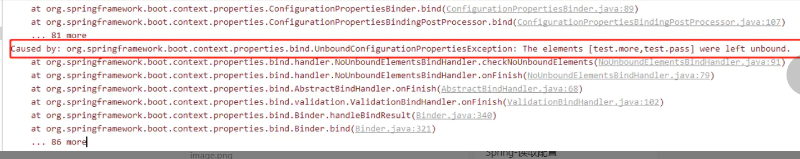
如果我们在 application.yml属性上定义的属性不能被正确的解析会发生什么?假如我们为原本应该为布尔值的属性提供的值为 'pass':
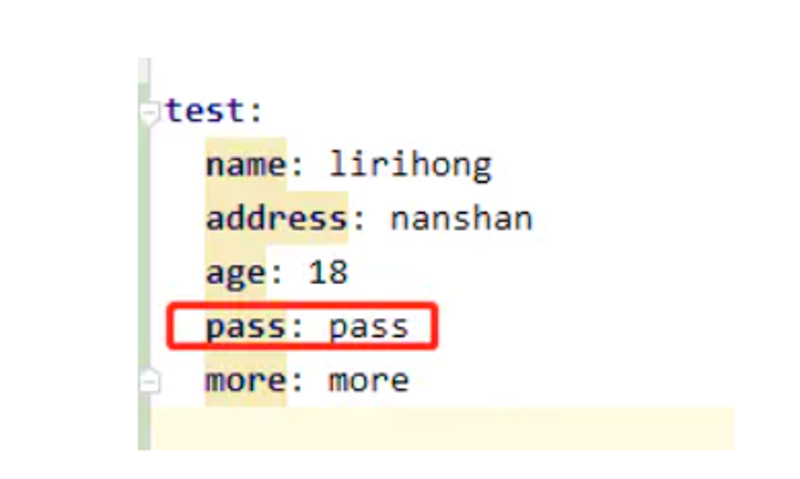
但是需要的是一个boolean 的值

默认情况下,Spring Boot 将会启动失败,并抛出异常:

--end--